
Robotics is an interdisciplinary research area at the interface of computer science and engineering. Robotics involves design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design intelligent machines that can help and assist humans in their day-to-day lives and keep everyone safe.
Robotics draws on the achievement of information engineering, computer engineering, mechanical engineering, electronic engineering and others.
Power source
At present, mostly (lead–acid) batteries are used as a power source. Potential power sources could be: Pneumatic (compressed gases), Solar power, Hydraulics (liquids), Flywheel energy storage, Organic garbage (through anaerobic digestion), Nuclear.
Actuation
Actuators are the "muscles" of a robot, the parts which convert stored energy into movement. Various component used for Actuators are Electric Motors, Linear Actuators, Series Elastic Actuators, Air Muscles, Muscle Wires, Electroactive Polymeers, Peizo Motors, Elastic Nanotubes.
Sensing
Sensors allow robots to receive information about a certain measurement of the environment, or internal components. Various types of this area are Touch, Vision, Other (such as lidar, radar, and sonar - Lidar measures distance to a target by illuminating the target with laser light and measuring the reflected light with a sensor. Radar uses radio waves to determine the range, angle, or velocity of objects. Sonar uses sound propagation to navigate, communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water.)
Manipulation
An agent’s control of its environment through selective contact. Robots need to manipulate objects; pick up, modify, destroy, or otherwise have an effect. Different manipulation objects are Mechanical grippers, Suction end-effectors, and General purpose effectors.
Locomotion
Locomotion is the mechanism that makes a robot capable of moving in its environment. Various types of locomotion are Rolling robots, Two-wheeled balancing robots, One-wheeled balancing robots, Spherical orb robots, Six-wheeled robots, Tracked robots, Walking applied to robots, Dynamic balancing, Passive dynamics, Flying, Snaking, Skating, Climbing, Swimming, Sailing.
Environmental interaction and Navigation
Though a significant percentage of robots in commission today are either human controlled or operate in a static environment, there is an increasing interest in robots that can operate autonomously in a dynamic environment. These robots require some combination of navigation hardware and software in order to traverse their environment. Various interaction methods are Human-robot interaction, Speech recognition, Robotic voice, Gestures, Facial expression, Artificial emotions, Personality, Social Intelligence.
Notes : Each component of Robots (as above said) has its own domain area and has its own applications. For example below are the different application of Computer Vision which is part of Sensors.
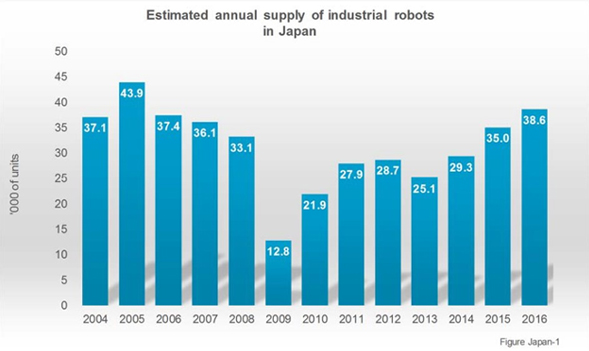

Industrial Robots
The first robots were industrial robots which replaced human workers performing simple repetitive tasks. Factory assembly lines can operate without the presence of humans, in a well-defined environment where the robot has to perform tasks in a specified order, acting on objects precisely placed in front of it The first robots were industrial robots which replaced human workers performing simple repetitive tasks. Factory assembly lines can operate without the presence of humans, in a well-defined environment where the robot has to perform tasks in a specified order, acting on objects precisely placed in front of it.
Autonomous Mobile Robots
Fully autonomous mobile robots do not rely on an operator, but instead they make decisions on their own and perform tasks, such as transporting material while navigating in uncertain terrain (walls and doors within buildings, intersections on streets) and in a constantly changing environment (people walking around, cars moving on the streets). The first mobile robots were designed for simple environments, for example, robots that cleaned swimming pools or robotic lawn mowers. The first mobile robots were designed for simple environments, for example, robots that cleaned swimming pools or robotic lawn mowers. Many autonomous mobile robots are designed to support professionals working in structured environments such as warehouses.
Humanoid Robots
Humanoid robots are a form of autonomous mobile robot with an extremely complex mechanical design for moving the arms and for locomotion by the legs. Humanoid robots are used for research into the mechanics of walking and into human-machine interaction. Humanoid robots have been proposed for performing services and maintenance in a house or a space station. They are being considered for providing care to the elderly who might feel anxious in the presence of a machine that did not appear human. On the other hand, robots that look very similar to humans can generate repulsion, a phenomenon referred to as the uncanny valley.
Educational Robots
Advances in the electronics and mechanics have made it possible to construct robots that are relatively inexpensive. Educational robots are used extensively in schools, both in classrooms and in extracurricular activities. Many educational robots are designed as pre-assembled mobile robots. An important advantage of these robots is that you can implement robotic algorithms “out of the box,” without investing hours in mechanical design and construction.
Industries
Robots are used for handling material, cutting, welding, color coating, drilling, polishing, etc.
Military
Autonomous robots can reach inaccessible and hazardous zones during war.
Medicine
The robots are capable of carrying out hundreds of clinical tests simultaneously, rehabilitating permanently disabled people, and performing complex surgeries such as brain tumors.
Exploration
The robot rock climbers used for space exploration, underwater drones used for ocean exploration are to name a few.
Entertainment
Disney’s engineers have created hundreds of robots for movie making.